...
The fields in GitHub issues and pull requests mean the following in the EdgeX Foundry repositories:
Field | Definition |
author | An audit field that is automatically set to the creator of the issue or PR. |
title | A brief summary of the contents of the issue or pull request
Business rules: · Required always |
description | The first comment box after the title is the description. It provides the long description regarding what the issue or pull request is about. For pull requests, the description contains the body of the commit message and additional metadata used by GitHub for automation purposes, such as "Fixes #" tags.
Business rules: · Required always |
comments | Every comment box after description forms a running log of the community discussion of the issue or pull request. Diagnostic information from automation or bots may appear in comments as well. |
assignees | If assigned, the assignee has assumed responsibility and is the point of contact for coordinating work on the issue. The assignee must be a project member. For pull requests, this field has no special meaning: if set, it is usually set to the author. Business rules: · Required for all in-progress issues · Recommended for all release backlog issues |
reviewers | (Pull requests only.) List of project members who are solicited to review the pull request. |
labels | Labels are used to implement virtual fields. See "Virtual Field Definitions" below. |
projects | Projects are used by EdgeX working groups to subscribe to the status of an issue on their project board. One of these working groups is responsible for managing the Issue through its lifecycle. An Issue may be on multiple boards simultaneously. |
milestone | All milestones in EdgeX refer to releases. The milestone field is used to include the issue in this release's backlog. It indicates a commitment to resolve the issue by the named milestone. (For retroactive milestones, it would be used to flag the issue as "wontfix".) Milestone is a single-select field: only one milestone can be selected at a time. |
Table 1: Issue and Pull Request Field Definitions
...
The "labels" field is used to implement virtual fields. All virtual fields are optional unless otherwise specified. These are defined as follows:
Virtual Field | Definition |
issue_type | Indicates the type of issue (single-select):
Business rules:
|
close_reason | Explains why an issue was closed (without a fix) (single-select):
Business rules:
|
subsystem_affected | Indicates the scope of the proposed change (multiple-select):
|
release_affected | A multiple-select field used for bugs only that indicates a release of EdgeX which is affected by the issue. Note, there may be multiple release_affected labels if the issue exists in more than one EdgeX release. For feature development work, the milestone field is the official field used for release planning. (This changes the current practice so there will be a transition period where both fields are used.) If multiple release_affected tags exist and the issue is only fixed in one of these releases resulting in the issue being closed, if any of affected releases is either an active development release or an LTS release, then a new issue should be opened with release_affected set accordingly. This allows the issue to continue to be tracked in the other affected releases where it makes sense to do so. Values:
Business rules:
Exceptions:
|
exception | Indicates an exceptional condition outside of the normal workflow (multiple-select):
|
priority | Priority is used to influence where to put resources and what features to cut when a release window is closing (single-select). The permissible values for priority and suggested guidance around their usage are:
|
Table 2: Virtual field definitions
...
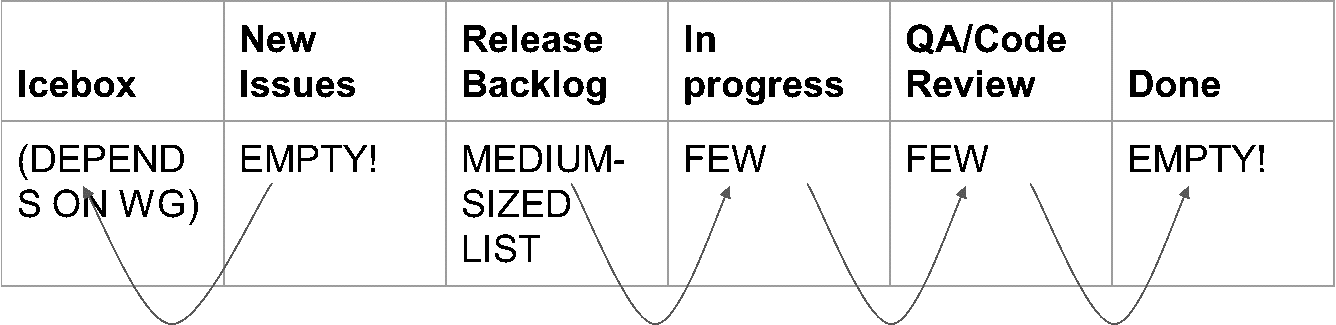
There is no "status" field in GitHub. Issues are either "open" or "closed". However, issues may be assigned to project Kanban boards and can be moved from column to column in order to provide advanced status reporting. The current column of an issue is represented below as "status." Issues may freely move from state to state without restriction. Moreover, each working group may have its own customized state machine. The table presented below is the project-recommended values. Unless otherwise specified, issues must be manually moved from state to state.
Status | Meaning |
new issue | Default state for incoming issues when assigned a project. New issues require triage into either "icebox" or "release backlog" status. |
icebox | There are no current plans to work on the issue in the near-term. |
release backlog | The issue is planned for the upcoming release or be retroactively fixed for a previous release. |
in progress | Someone has started working on the issue |
QA/Code Review | A state reserved for pull requests that have not been approved. GitHub automation automatically places new pull requests here. |
Done | Terminal state for all issues and pull requests. GitHub automation will move issues and pull requests here automatically when they are closed. |
Table 3: Project-recommended issue status values
...
From this point forward, issues gradually transition to the "done" state:
Attachments
| Attachments | ||
|---|---|---|
|